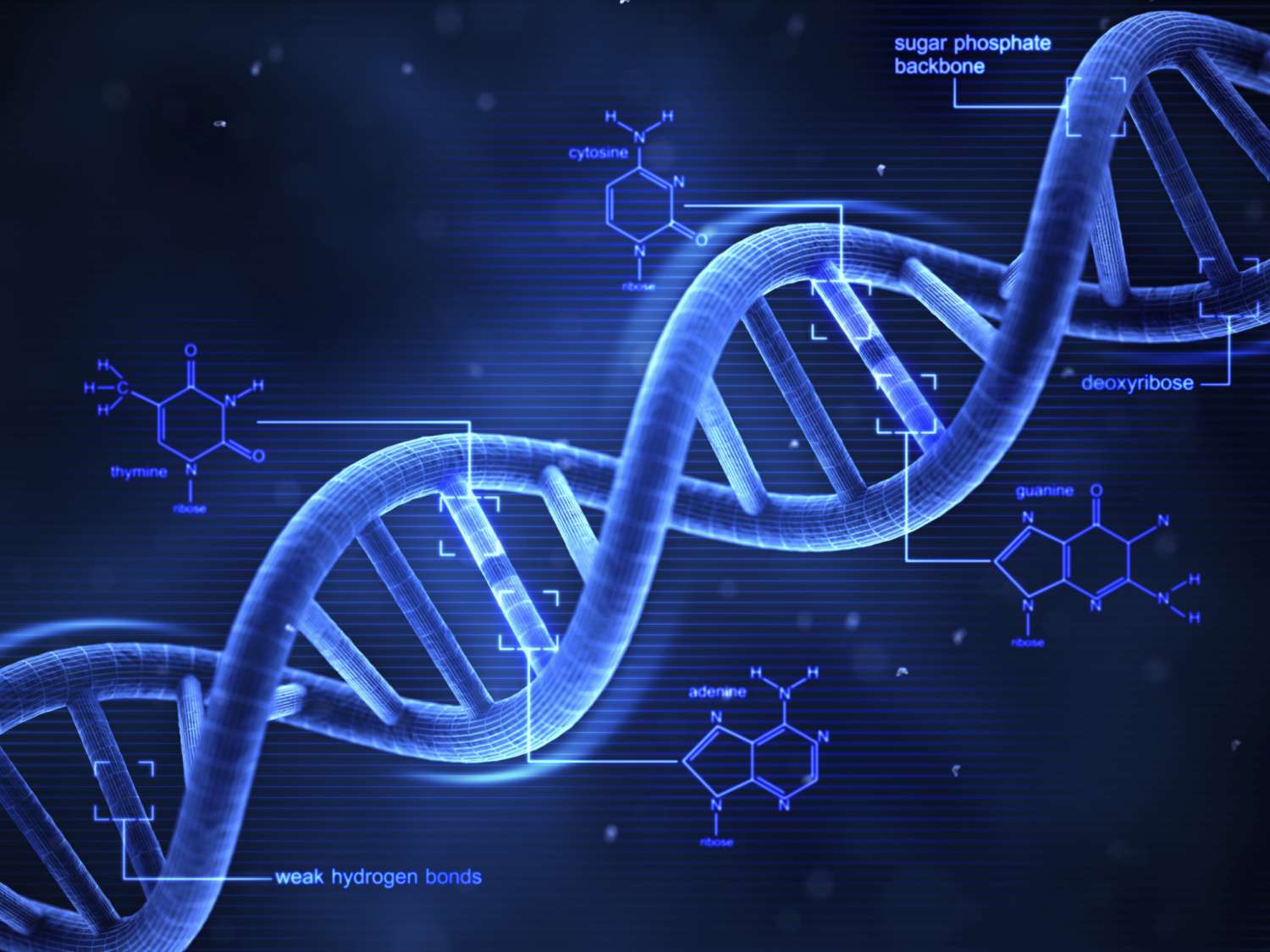
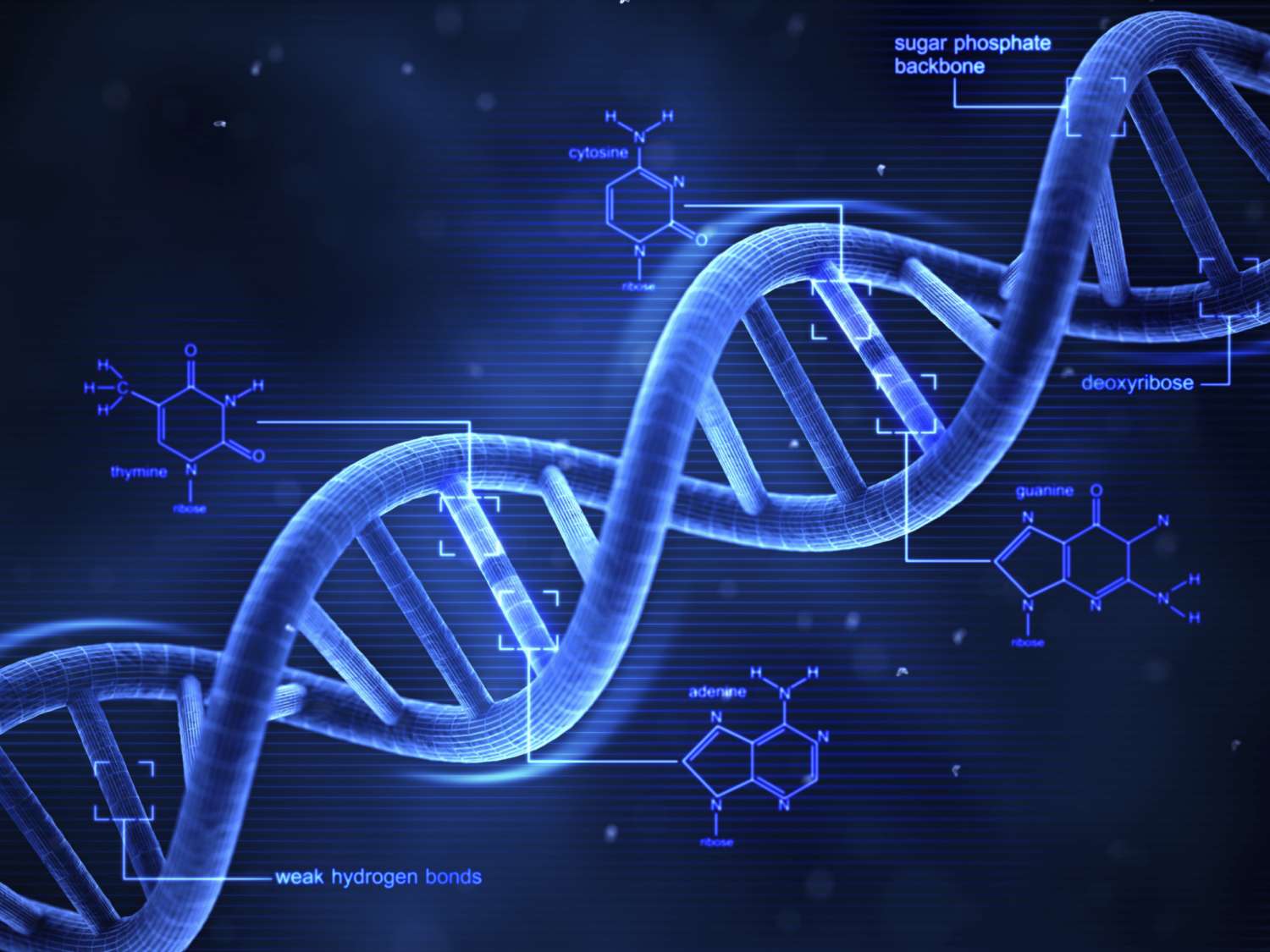
In simple terms, genes are the basic unit of inheritance. They are a segment of the DNA that gives a set of instructions to synthesize a protein.
DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, is made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides have a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar called ribose and a phosphate. DNA has a double helix structure, meaning that there are two linear strands running antiparallel to each other and are twisted together. There are four different nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). In DNA, these nitrogenous bases are in pairs, A with T and C with G. They are called complementary base pairs.
In protein synthesis, DNA is ‘unzipped’ and a genetic sequence is exposed. From the exposed area, a ribonucleic acid (RNA) strand is produced through complementary base pairing. Unlike DNA, RNA does not have the thymine base, instead, it is replaced by uracil (U). The newly formed RNA is called messenger RNA (mRNA) and carries the genetic code for protein synthesis. mRNA attaches to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place. Another molecule, transfer RNA (tRNA), carries an amino acid, the basic unit of proteins, on one end and three unpaired bases, the anticodon, on the other. In the ribosome, the first three bases, or codon, of the mRNA is paired with the complementary tRNA. This process is continued with the adjacent codons until a termination codon is exposed. The amino acids carried by the tRNA are bonded with each other through peptide bonds to create a polypeptide.
Multiple polypeptides form a protein. For example, the protein that gives red blood cells its prominent red color is haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is spherical due to the protein having hydrophilic polypeptides facing outward and hydrophobic polypeptides facing inward. Sickle cell anemia, which is a genetic disorder, caused by a mutation where the correct sequence of bases in the DNA should be CTC but is changed to CAC. CTC codes for glutamic acid in the hydrophilic polypeptide but is replaced with CAC which codes for valine. Valine is hydrophobic, which causes the haemoglobin to become less soluble and the red blood cell takes the shape of a sickle.
In conclusion, genes are responsible for every trait that you, your friends, family and everyone else has. One small tweak in your DNA can have a myriad of outcomes, from having blue eyes to severe health complications.
Leave a Reply